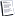
This was posted on Still's forum, it's Greek to me, but maybe one of you younger guys might make some sense of it.
Norm
It's a bad certificate error. This likely a configuration issue with the ISP who hosts the forums.
More info:
"What does this mean?
We were able to retrieve a certificate for this site, but the domain names listed in it do not match the domain name you requested us to inspect. It's possible that:
The web site does not use SSL, but shares an IP address with some other site that does.
The web site no longer exists, yet the domain name still points to the old IP address, where some other site is now hosted.
The web site uses a content delivery network (CDN) that does not support SSL.
The domain name is an alias for a web site whose main name is different, but the alias was not included in the certificate by mistake. "
"Why is my certificate not trusted?
There are many reasons why a certificate may not be trusted. The exact problem is indicated on the report card in bright red. The problems fall into three categories:
Invalid certificate
Invalid configuration
Unknown Certificate Authority
1. Invalid certificate
A certificate is invalid if:
It is used before its activation date
It is used after its expiry date
Certificate hostnames don't match the site hostname
It has been revoked
It has insecure signature
It has been blacklisted
2. Invalid configuration
In some cases, the certificate chain does not contain all the necessary certificates to connect the web server certificate to one of the root certificates in our trust store. Less commonly, one of the certificates in the chain (other than the web server certificate) will have expired, and that invalidates the entire chain.
3. Unknown Certificate Authority
In order for trust to be established, we must have the root certificate of the signing Certificate Authority in our trust store. SSL Labs does not maintain its own trust store; instead we use the store maintained by Mozilla.
If we mark a web site as not trusted, that means that the average web user's browser will not trust it either. For certain special groups of users, such web sites can still be secure. For example, if you can securely verify that a self-signed web site is operated by a person you trust, then you can trust that self-signed web site too. Or, if you work for an organisation that manages its own trust, and you have their own root certificate already embedded in your browser. Such special cases do not work for the general public, however, and this is what we indicate on our report card.
4. Interoperability issues
In some rare cases trust cannot be established because of interoperability issues between our code and the code or configuration running on the server. We manually review such cases, but if you encounter such an issue please feel free to contact us. Such problems are very difficult to troubleshoot and you may be able to provide us with information that might help us determine the root cause.
SSL Report v1.36.1"
|